What is Bluetooth and How its emerging in AV Industry? Will Bluetooth Auracast change the Audio playback in public domain?
Related Content
891643783
Bluetooth operates on the 2.4 GHz frequency band and uses a technique called frequency hopping spread spectrum to minimize interference from other devices. It uses a radio communication protocol to transmit data between devices, and it can operate in two modes: master mode and slave mode.
In the AV industry, Bluetooth is used to enable wireless connectivity between devices such as:
- Audio devices: Bluetooth speakers, headphones, and soundbars can connect to devices like smartphones, tablets, and laptops.
- Audio systems: Bluetooth amplifiers, receivers, and transmitters can be used to distribute audio signals wirelessly.
- AV equipment: Bluetooth-enabled projectors, displays, and conferencing systems can be used to connect devices wirelessly.
Bluetooth is emerging in the AV industry for several reasons:
- Convenience: Bluetooth allows for easy and convenient connectivity between devices, eliminating the need for cables and wires.
- Flexibility: Bluetooth-enabled devices can be easily moved or repositioned without having to rewire or replug them.
- Cost-effectiveness: Bluetooth technology is often less expensive than traditional wired connections.
- Increased demand: With the increasing use of mobile devices and streaming services, there is a growing demand for wireless connectivity solutions in the AV industry.
- Improved user experience: Bluetooth enables seamless connectivity and switching between devices, providing a more intuitive and user-friendly experience.
Some examples of Bluetooth-enabled AV products include:
- Wireless audio speakers that can connect to smartphones or tablets via Bluetooth.
- Bluetooth-enabled soundbars that can receive audio signals from TVs or streaming devices.
- Wireless microphones that can transmit audio signals to a central receiver or amplifier via Bluetooth.
- Bluetooth-enabled projectors that can receive audio signals from laptops or smartphones via Bluetooth.
In summary, Bluetooth is a wireless technology that enables devices to communicate with each other over short distances. In the AV industry, Bluetooth is emerging as a popular solution for wireless connectivity, offering convenience, flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and improved user experience.
There are currently several versions of Bluetooth devices, each with its own set of features and improvements. Here are the current versions of Bluetooth devices:
- Bluetooth 5.0 (Released in 2016): This version offers improved range, speed, and capacity for data transmission. It has a range of up to 4 times farther than Bluetooth 4.2 and can transmit data at speeds of up to 2 Mbps.
- Bluetooth 5.1 (Released in 2019): This version is an extension of Bluetooth 5.0, offering improved location services, direction finding, and broadcast data transmission. It also provides better coexistence with other wireless technologies.
- Bluetooth 5.2 (Released in 2020): This version focuses on improving the performance and reliability of Bluetooth connections. It includes new features such as LE Audio, which allows for multiple audio streams and better audio quality.
- Bluetooth 5.3 (Released in 2021): This version is an incremental update to Bluetooth 5.2, offering improved security features and better support for IoT devices.
Some of the key features of these Bluetooth versions include:
- Long-range capabilities: Bluetooth 5.0 and later versions offer longer range and better penetration through walls and other obstacles.
- Higher data transfer speeds: Bluetooth 5.0 and later versions offer faster data transfer speeds, making it possible to transfer larger files and enjoy smoother audio streaming.
- Improved security: Bluetooth 5.0 and later versions offer improved security features, including encryption and authentication protocols.
- Multiple audio streams: Bluetooth 5.2 and later versions support multiple audio streams, allowing for simultaneous playback of different audio sources.
- LE Audio: Bluetooth 5.2 and later versions support LE Audio, which enables low-power audio streaming and improved audio quality.
It's worth noting that not all devices support the latest versions of Bluetooth, so it's essential to check the specifications of your device to determine which version of Bluetooth it supports.
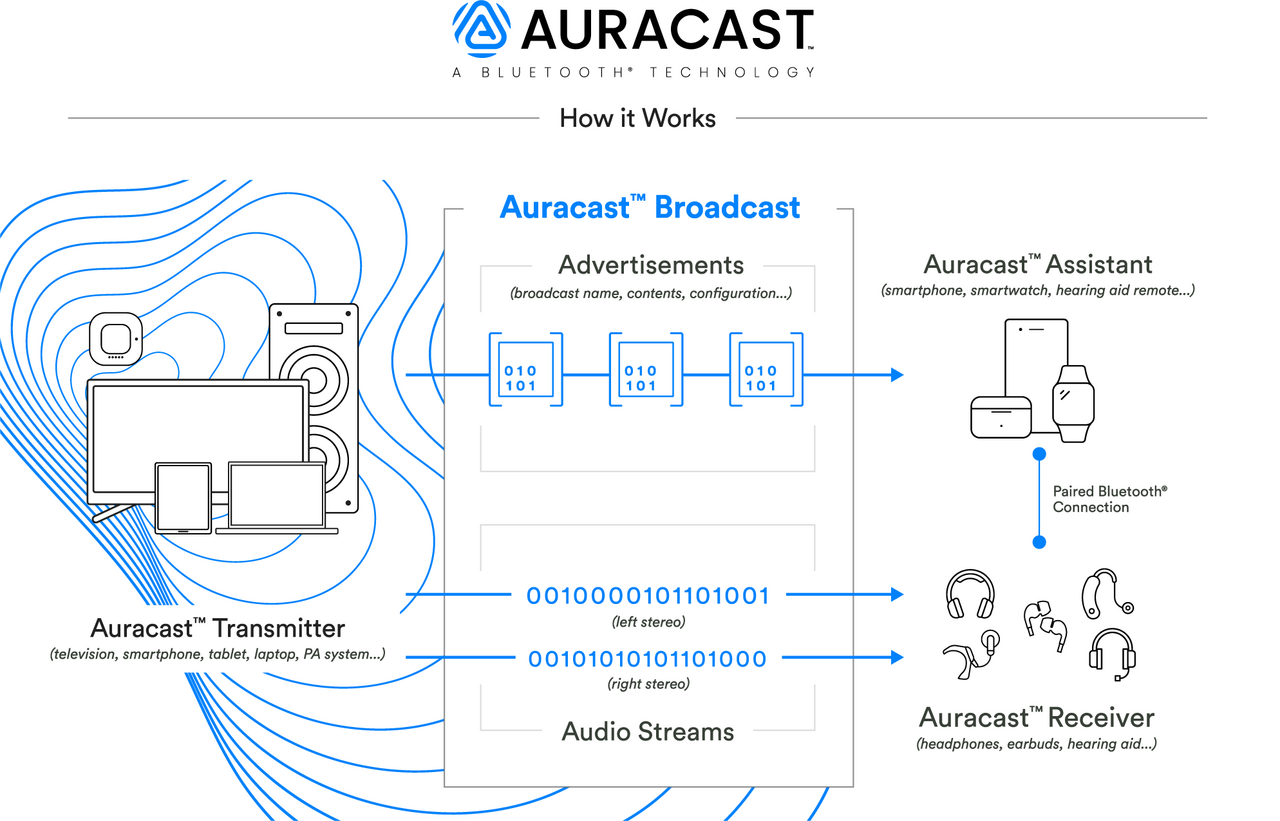
Auracast is a new technology that allows audio broadcasts to be transmitted over Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and other wireless technologies, making it possible for public spaces to offer high-quality, immersive audio experiences to their visitors. Here's a breakdown of what Auracast is and how it will enable audio broadcasting in public domains:
What is Auracast?
Auracast is an open standard for audio broadcasting over wireless networks, developed by the Wireless Power Consortium (WPC), a group of companies that includes Sony, Intel, and others. It's designed to provide a reliable and secure way for devices to receive audio signals over short-range wireless connections.
How does Auracast work?
Auracast uses a combination of technologies to enable audio broadcasting in public spaces:
- Audio transmission: An Auracast-enabled device (such as a receiver or a gateway) transmits the audio signal over Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or other wireless technologies.
- Audio encoding: The audio signal is encoded using a specific algorithm to ensure high-quality transmission and reception.
- Device discovery: Devices with Auracast capabilities can detect and connect to nearby Auracast-enabled devices, allowing them to receive the audio signal.
- Secure authentication: Auracast uses encryption and authentication mechanisms to ensure secure and authorized access to the audio signal.
How will Auracast enable audio broadcasting in public domains?
With Auracast, public spaces can offer a variety of immersive audio experiences, including:
- Wireless audio tours: Visitors can use their smartphones or headphones to receive guided tours or audio descriptions of art exhibits, museum collections, or public landmarks.
- Indoor navigation: Auracast-enabled devices can provide users with location-based audio cues, helping them navigate public spaces like shopping malls, airports, or museums.
- Public events: Public spaces can broadcast live events, such as concerts, lectures, or sports games, to attendees using their personal devices.
- Wayfinding: Auracast can help people with visual impairments navigate public spaces more easily by providing auditory cues and directions.
Benefits of Auracast
The benefits of Auracast include:
- Improved accessibility: Auracast enables people with disabilities to access audio content more easily.
- Enhanced user experience: Public spaces can offer more engaging and interactive experiences for visitors.
- Increased revenue: Public spaces can monetize their audio content through advertising or sponsored content.
- Simplified setup: Auracast-enabled devices can be easily installed and configured, reducing the need for complex wiring or infrastructure changes.
Overall, Auracast has the potential to revolutionize the way public spaces share audio content with their visitors, making it more accessible, engaging, and enjoyable.
-
Xchange Advocates are recognized AV/IT industry thought leaders and influencers. We invite you to connect with them and follow their activity across the community as they offer valuable insights and expertise while advocating for and building awareness of the AV industry.





Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on AVIXA Xchange, please sign in
I’m actually very excited to see how this has evolved. The ability to replace physical cables alone provides more room for creativity when designing audio systems. But for me personally, I don’t have very pleasant experiences with traditional bluetooth technology, mostly because of the unstable connection and audio signal quality. But with LE Audio, I bet this will not be an issue anymore.
I’m very keen to try Auracast in lecture hall setting with mix minus configuration. I’m wondering if there’s any real life use case I can study and benchmark?
p/s: Imagine wireless power transmission application in AV industry, good or bad?