Sound absorption: what is it and how does it work?

It is a subject that is largely unknown and that can change the way you work, live in your home or socialise with your friends in your leisure time. The acoustic absorption or sound acoustic is the great overlooked element in space planning, and today we're shedding light on the main questions surrounding this field.
Sound absorption is defined as the ability of all materials to absorb a portion of the energy of sound waves when they strike them, thereby reducing the amount of sound energy that is reflected by the material.
To give you an idea of how this works, when a sound wave hits one of the surfaces in a room, some of this sound energy is reflected and some penetrates the surface. In turn, this penetrating energy is either absorbed by the material and converted into heat energy, or transmitted to other rooms, or reflected.
In short, the greater the absorptive capacity of the materials in the space, the greater the absorption of the sound and the sound propagation through the space will be reduced.
The sound absorbing properties of a material are expressed in the sound absorption coefficient, α (alpha) ranges from 0 / 0% (total reflection) to 1 / 100% (total absorption). It can be said that:
- Absorption increases with frequency.
- For high frequencies the absorption does not depend on the thickness of the material.
- For low frequencies the absorption increases with thickness.
- Different material densities facilitate absorption at different frequencies. Because the absorption coefficient of a material varies with frequency, it is usually specified at frequencies of 125, 250, 500, 1000, 1000, 2000 and 4000 Hz. The edge effect or diffraction effect is produced by wave diffraction at the edges of the material to be measured, so that in this case the sound absorption can be greater than 1.
What is the difference between sound insulation and sound absorption?
By acoustic insulation we understand the ability to limit the transmission of sound between two environments. Its main purpose is to prevent sound from propagating from one place to another, either to maintain privacy or to prevent the entry of unwanted noise. It is achieved through the use of materials and techniques that block or reduce sound transmission, such as walls and ceilings with high insulation ratings, double-glazed windows and doors with airtight seals.
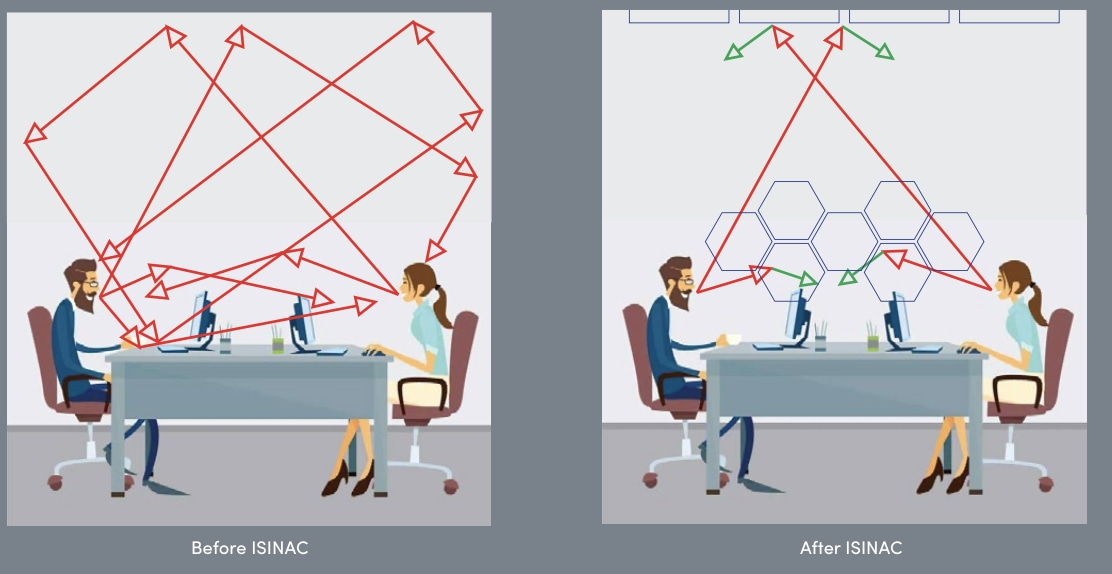
With regard to the acoustic absorption refers to the improvement of acoustic comfort within a given space. The main objective of sound absorption is to control reverberation, which is the phenomenon of prolongation and mixing of sound echoes in an enclosed environment. Through the use of acoustic absorbing materials, such as acoustic wall panels. The amount of sound reflected from surfaces is reduced, which reduces reverberation and improves the clarity of the sound in the room.
How do we know which acoustic absorbing panels suit what we are looking for?
At ISINAC we have several options in terms of acoustic panels. We have solutions for the sector professional, a range excellence designed for demanding environments, mobile solutions for offices or curtains acoustic, among many others.
The example of the curtains illustrates the versatility of ISINAC products. These are specially designed products made of materials that not only have an absorption of 100% (Alpha sabine 1 and NRC 1), but also sound insulation of 9 decibels. As a result, there is a significant increase in acoustic comfort and all with environmentally friendly materials.
Ready to completely change your space? Welcome to acoustic comfort!
Recommended Content
Creating the Next Generation AV Workforce: From Audio Engineers to Solution Designers

End 2025, Enter 2026 (AV Industry)






Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on AVIXA Xchange, please sign in