New testing shows significant reduction in expected service life for edge-lit LCD displays

Image Credit: DC Studio
New findings are showing a significant reduction in service life for certain displays, according to testing conducted by reporters at RTINGS.com. The findings in question specifically affect edge-lit LCD displays, comparing and contrasting how the issue manifests between manufacturers. While manufacturers will commonly test displays to an average of 10,000 hours, the findings show that some models begin exhibiting problems as early as 2,200 hours of service.
Edge-lit displays function exactly as they sound: By placing a concentrated amount of LEDs at the edge of the display, then passed through an adaptive medium that spreads the light evenly throughout the display. Different manufacturers have different methods of construction for edge-lit displays, such as focusing LEDs on one side of the display or evenly distributing them around the edges. Regardless of these differences, as well as the practice of including heat sinks in construction, the displays all showed a significant decrease in expected service life.
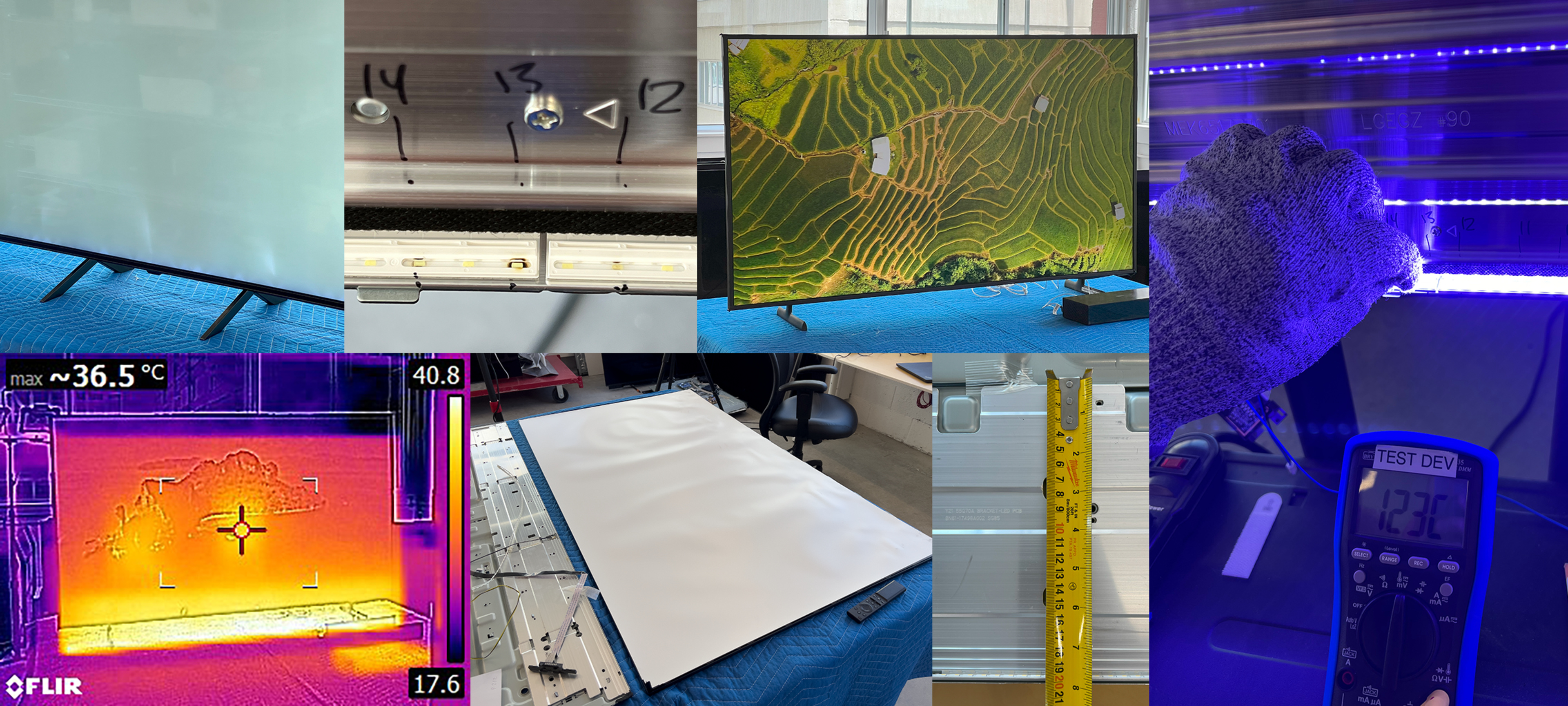
Researchers conducted extensive testing across brands. Source: RTINGS.com
LEDs have the benefit of both being bright and energy-efficient, making them the light source of choice for displays. The biggest downside they exhibit, however, is the heat they generate during use, as about 70 percent of the energy used to power an LED turns into heat. LEDs are still cooler and more efficient than other lighting technology, but the heat generated causes nearby components within the display to suffer from heat-induced warping. This affects key components, such as the adaptive lighting medium and the LEDs themselves, with both exhibiting signs of significant cumulative damage, degrading the picture. According to the report, this is not an isolated incident, but potentially an intrinsic flaw.
Researchers posited that these displays inherently fail sooner because of the overall form factor of the product. Thin displays naturally have components that are positioned closer together, putting them at greater risk of heat damage as a result. Despite these concerns and risks, manufacturers have been able to achieve designs that greatly minimize the amount of space required for displays, serving a wide variety of consumers and businesses as they seek solutions.
In response to inquiries about the findings, manufacturers have uniformly stood by their assertions of improving their products as technology advances. Manufacturers continue to gravitate towards advancements in LED technology, including miniLED and microLED, to improve picture quality and heat dissipation. Nevertheless, being informed of all aspects of a product's performance bolsters the confidence of a prospective buyer, whether it's a consumer purchasing a TV or a pro AV designer considering use cases for a space or product.






Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on AVIXA Xchange, please sign in
Despite the advancements in LED technology, such as miniLED and microLED, aimed at improving heat dissipation and picture quality, it remains essential for manufacturers to address these inherent challenges to ensure reliability and longevity in both consumer and professional applications.